This set of exercises, called the Brandt & Daroff exercises, is used to treat the disturbing problem of benign positional vertigo.
They are specifically designed to treat those cases in which the cause is considered to be clumps of debris (like fine sediment) collecting in one of the canals of the inner ear.
The exercises disperse this debris away from the delicate balance membrane.
Rules
• Perform 3 times daily (if possible).
• Take about 10 minutes each time.
• Usually do 5 or more times to each side.
• They are beneficial only if dizziness is reproduced.
• Take antisickness tablets if nausea is a problem.
Method
1. Sit on the edge of bed; turn your head slightly to the left side (about 45°). Lie down quickly on the right side (ensure the back of the head rests on the bed). Wait for either 20 to 30 seconds or for any dizziness to settle.
2. Sit up straight. Wait for 20 to 30 seconds or for any dizziness to settle.
3. Repeat on the other side: turn the head slightly to the right side before lying down quickly on your left side.
Note:
• It doesn’t matter on which side you lie down first.
• Turn your head away from the side on which you lie down.
• It is important to reproduce dizziness with the exercises.
• If the exercises are done regularly, the symptoms should settle over a period of several days but this may vary from 3 to 4 days to weeks.
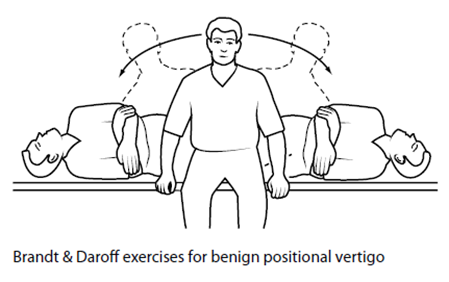
Steps for this excercise can be seen here
What are the precautions one must take before performing these excercises?
Precautions and contraindications to be aware of when performing Brandt & Daroff exercises:
Severe Dizziness: If you are experiencing severe dizziness, it may not be safe to perform these exercises. It’s important to seek medical advice before starting any new exercise program.
Neck or Back Pain: If you have neck or back pain, it’s important to speak with your doctor before performing these exercises, as they may worsen your symptoms.
Recent Head Injury: If you have recently suffered a head injury, it’s important to wait until you have fully recovered before starting these exercises.
Inner Ear Infection: If you have an inner ear infection, it’s important to wait until the infection has cleared before performing these exercises.
Cardiovascular or Respiratory Issues: If you have a history of cardiovascular or respiratory issues, it’s important to speak with your doctor before starting these exercises, as they may be more difficult for you.
It’s important to perform the exercises slowly and smoothly to avoid any sudden movements that could worsen your vertigo symptoms. If you experience any dizziness or discomfort during the exercises, stop and seek medical advice.
Are there any other methods and how they compare with Brandt & Daroff exercises?
The Epley and Semont techniques are alternative exercises used to alleviate vertigo symptoms.
While it is acceptable to attempt the Brandt-Daroff exercises at home, it is crucial that your doctor demonstrates how to perform the Epley and Semont maneuvers correctly before attempting them independently.
Your doctor may advise against performing the Epley maneuver at home due to its potential to compress arteries and induce vomiting.
Compared to other similar exercises, many individuals find the Brandt-Daroff exercises to be easier to perform at home and safer for those with back or spine injuries.
For some individuals, the Epley and Semont maneuvers are slightly more effective than the Brandt-Daroff exercises and take less time to complete.
To know more about this condition and discuss treatment options you can book appointment with doctor.
- Note –This is a condensed summary of diagnostic, therapeutic, and medication information and is not intended to be exhaustive. It serves as a guide to aid in understanding potential diagnostic and treatment options and should not be considered a complete source of information. It does NOT encompass all details regarding conditions, treatments, medications, side effects, or potential risks that may be relevant to a particular individual. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, which is based on a doctors assessment of a patient’s unique health status after examining them. To receive comprehensive information about their health, medical queries, and treatment options, including the risks and benefits of medication use, patients should consult a doctor. This information does not guarantee the safety, efficacy, or approval of any treatment or medication for a specific patient.