What is trigeminal neuralgia?
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a condition that causes sudden and severe pain in parts of the face.
The trigeminal nerve, a nerve that connects the brain to the face, is the source of TN.
What are the symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia?
Attacks of TN are characterised by stabbing, severe pain in the cheek, lower face, or eye area. The pain typically only affects one side of the face and lasts for a few seconds to several minutes. Attacks could take place repeatedly. Often, certain movements or activities make the pain attacks happen. These can include:
●Touching the face
●Chewing
●Talking
●Brushing the teeth
●Smiling or frowning
●Cold air on the face
TN can also cause muscle spasms in the face, along with pain.
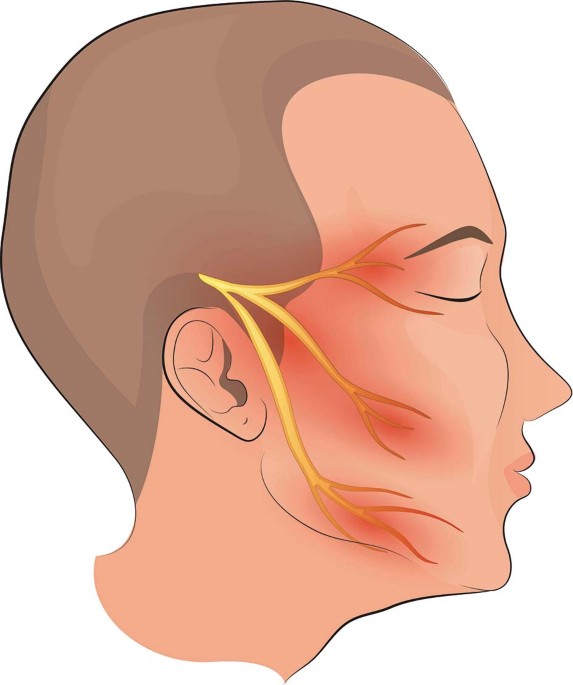
Who is at risk for trigeminal neuralgia?
It is found more often in women than in men (ratio 1.74:1) and is most common from 50 to 69 years of age[5]. Hypertension, arteriosclerotic vascular changes, aging, individual sensitivity, and familial history are important risk factors for trigeminal neuralgia
What are Triggers of pain for trigeminal neuralgia?
Some common triggers include eating, talking, brushing teeth, cold, shaving and light touches to the face. If you can’t figure out what’s causing your pain, it may be helpful to keep a pain diary in which you record key details of your environment and activity in order to look for common threads among different symptom flare-ups. It is very important that you identify these common triggers in your case and try best to avoid them.
Will I need tests?
Maybe. Your doctor should be able to tell if you have TN by learning about your symptoms and doing an exam.
They might do tests to get more information about your TN or what’s causing it. These tests can include an MRI or CT scan of your brain. These are imaging tests that can create pictures of your brain
Can a blood test detect trigeminal neuralgia?
No , trigeminal neuralgia is not detected by blood tests.
How is trigeminal neuralgia treated?
TN is usually treated with medicine. Doctors use different types of medicines to treat TN. Most often doctors prescribe a type of medicine normally used to prevent seizures. The one used most often to treat TN is called carbamazepine . There are several others, too. These medicines quiet the nerve signals that cause pain in TN.
For most people, the medicine helps reduce the number of TN attacks they have and makes their pain less severe. But if medicines don’t help enough or cause too many side effects, your doctor might talk with you about other treatment options. These include different types of surgical procedures that quiet the nerve and make it less likely to fire. These surgical treatments might help with symptoms, but side effects sometimes happen, including numbness or pain in the face.
Is trigeminal neuralgia lifelong?
Trigeminal neuralgia is usually a long-term condition. Episodes may last for weeks to months followed by pain free intervals. Painful episodes may recur. There could be variation in severity of painful episode with time.
Which fruit is good for nerves?
Berries, peaches, cherries, red grapes, oranges and watermelon, among others, are loaded with antioxidants, which help to decrease inflammation and reduce nerve damage. Plus, grapes, blueberries and cranberries have been found to be full of a powerful anti-inflammatory compound
Is there something I can do to relieve my pain ?
While home remedies may not be capable of completely curing trigeminal neuralgia symptoms, they can be very useful for reducing severity of pain
Many people find relief from trigeminal neuralgia pain by applying heat to the affected area. You can do this locally by pressing a hot water bottle or other hot compress to the painful spot.
Cold may also help relieve the pain, although you’ll obviously want to avoid this remedy if you’re one of the many trigeminal neuralgia sufferers for whom cold triggers symptoms.
You can use an ice pack wrapped in a thin towel or pillowcase to numb the painful area. Keep the cold in contact with the affected area for about 30 seconds or until the area begins to feel numb.
Some trigeminal neuralgia sufferers find that switching between the hot and cold compresses helps more.
While many people find that a light touch — often as light as a gentle breeze wafting over their skin — can trigger trigeminal neuralgia symptoms, they also find that applying pressure to the area can help relieve symptoms. Use your entire hand to press on the affected area. You may need to apply a reasonable amount of pressure in order to get results.

To know more about this condition and discuss treatment options you can book appointment with doctor
- Note –This is a condensed summary of diagnostic, therapeutic, and medication information and is not intended to be exhaustive. It serves as a guide to aid in understanding potential diagnostic and treatment options and should not be considered a complete source of information. It does NOT encompass all details regarding conditions, treatments, medications, side effects, or potential risks that may be relevant to a particular individual. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, which is based on a doctors assessment of a patient’s unique health status after examining them. To receive comprehensive information about their health, medical queries, and treatment options, including the risks and benefits of medication use, patients should consult a doctor. This information does not guarantee the safety, efficacy, or approval of any treatment or medication for a specific patient.